
In the field of pediatric therapy, ensuring optimal mobility for children is a paramount concern. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide on the top 10 essential techniques for pediatric mobility training.
From adaptive equipment and strengthening exercises to balance training and gait training, this guide covers a range of therapeutic interventions.
Additionally, neurodevelopmental techniques, task-oriented training, aquatic therapy, virtual reality interventions, and home modifications are explored.
By implementing these techniques, therapists can empower children with the freedom to move and thrive.
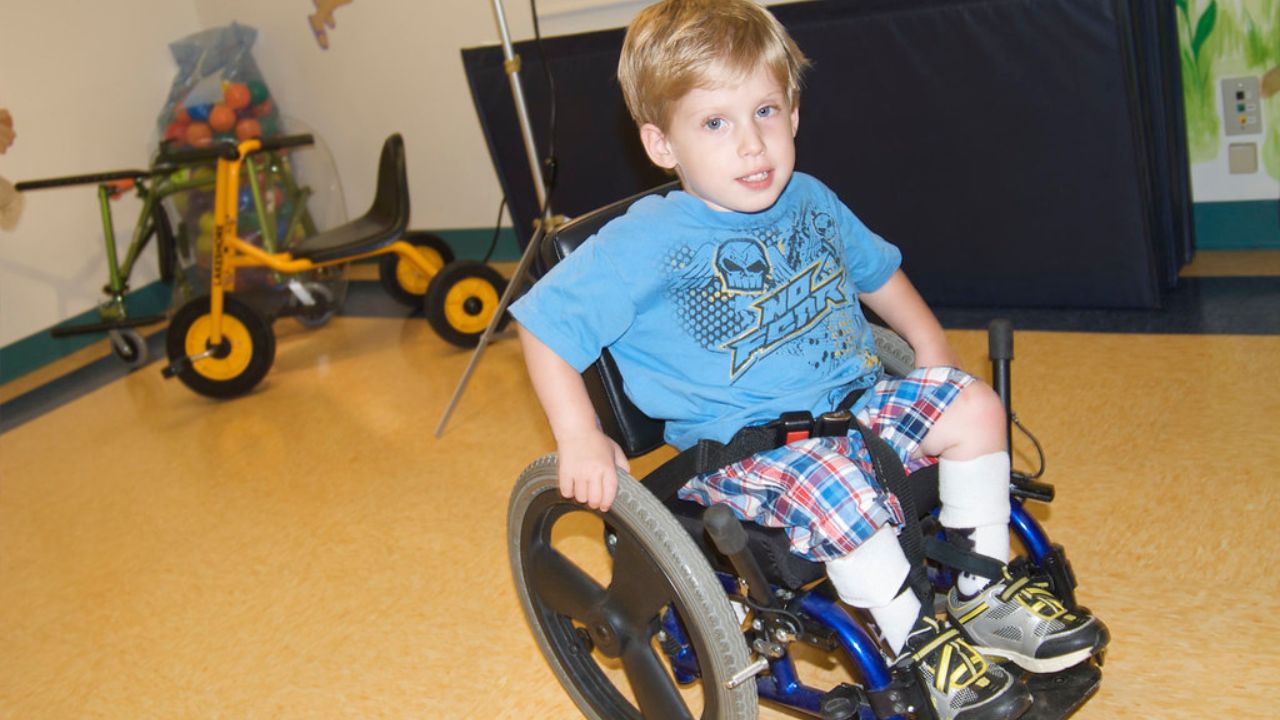
Adaptive Equipment
As therapists, it is important to consider the use of appropriate adaptive equipment in order to facilitate the optimal functional independence of our pediatric clients.
Adaptive equipment refers to devices or tools that are specifically designed to assist individuals with disabilities or limitations in performing daily activities. These tools can range from simple aids like grab bars and handrails, to more complex devices such as wheelchairs, walkers, and orthotics.
By incorporating adaptive equipment into our therapy sessions, we can empower our pediatric clients to overcome physical barriers and achieve greater mobility and independence.

In addition to adaptive equipment, therapists should also consider the importance of home modifications. Making modifications to the child's home environment can greatly enhance their ability to navigate and function independently.
This may involve installing ramps, widening doorways, or adding safety features like non-slip surfaces and grab bars. By creating a safe and accessible environment, we can help our pediatric clients thrive and participate fully in their daily activities.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises play a crucial role in pediatric mobility training. They target specific muscle groups and help improve overall strength and stability. By varying the resistance levels, therapists can tailor these exercises to each child's individual needs and capabilities.
Incorporating a variety of strengthening exercises into therapy sessions can promote muscle development and enhance functional abilities. This ultimately supports children in achieving their maximum potential.
Targeted Muscle Groups
By incorporating exercises that specifically target the muscle groups in need of rehabilitation, therapists can effectively improve mobility and functionality in pediatric patients. Targeted muscle group exercises not only help in muscle activation but also aid in correcting muscular imbalances and promoting overall strength and coordination.
Here are some essential techniques for targeting muscle groups in pediatric mobility training:
Isolated muscle exercises: Focusing on specific muscles allows for concentrated efforts in muscle activation and strength building.

Functional exercises: These exercises mimic real-life movements and help improve overall mobility and functionality.
Resistance training: Incorporating resistance bands or weights can provide added challenge and enhance muscle activation and growth.
Balance and stability exercises: These exercises engage the core and lower body muscles, improving balance and coordination.
Stretching and flexibility exercises: These exercises help maintain muscle length and joint mobility, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall flexibility.
Resistance Levels
Resistance levels can be adjusted according to the individual's strength and capabilities, ensuring progressive challenge and optimal muscle activation during strengthening exercises. This is especially important when working with the pediatric population, as their bodies are constantly growing and developing.
Pediatric mobility training requires a delicate balance between challenging the child's muscles and ensuring their safety. By adjusting the resistance levels, therapists can tailor the exercises to meet the child's specific needs and goals. This allows for gradual progression and prevents potential injuries.
It is crucial to consider the child's physical abilities and limitations when determining the appropriate resistance levels. By doing so, therapists can provide a safe and effective environment for children to develop their strength and mobility, empowering them to achieve their full potential and enjoy a life of freedom.

Balance Training
Balance training is an integral component of a comprehensive therapeutic intervention program aimed at improving stability and coordination in pediatric patients. It plays a crucial role in enhancing their overall mobility and reducing the risk of falls.
To effectively implement balance training, here are five essential techniques:
Balance assessment: Conducting a thorough evaluation of a child's balance capabilities to identify areas of improvement.
Core strengthening exercises: Engaging the core muscles to improve postural control and stability.
Proprioceptive training: Enhancing the child's awareness of their body position and movement through exercises like standing on unstable surfaces.
Dynamic balance activities: Including activities that challenge the child's balance while in motion, such as walking on a balance beam or playing catch while standing on one leg.
Fall prevention strategies: Teaching children how to recover from a loss of balance and providing them with strategies to avoid falls, like maintaining a wide base of support.

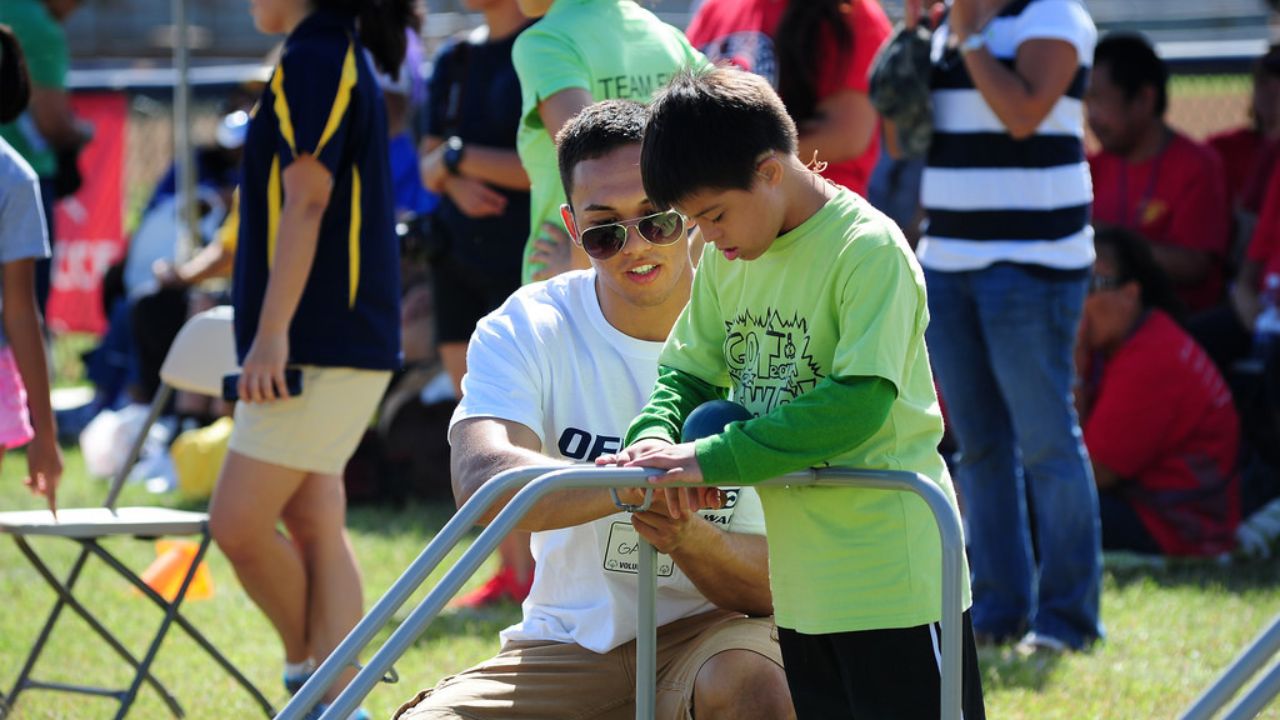
Gait Training
Gait training is an essential component of pediatric mobility training. It focuses on improving proper foot positioning, balance, and stability. By addressing these aspects, children can develop a more efficient and functional walking pattern. This enables them to navigate their environment with greater ease and independence.
Through targeted interventions and exercises, therapists can help children achieve optimal gait patterns. This enhances their overall mobility and quality of life.
Effective rehabilitation programs emphasize the importance of alignment, focusing on the optimal foot positioning for a stable foundation during ambulation. Proper foot positioning plays a crucial role in maintaining balance, preventing injuries, and improving overall mobility.
When it comes to foot alignment and shoe selection, here are five key considerations:
- Arch support: Look for shoes that provide adequate arch support to promote proper alignment and reduce strain on the feet.
- Toe room: Ensure that there is enough space for the toes to move freely, preventing discomfort and potential deformities.
- Heel stability: Opt for shoes with a firm and supportive heel counter to maintain stability during walking or running.
- Cushioning: Select shoes with sufficient cushioning to absorb shock and minimize impact on the feet and joints.
- Flexibility: Choose shoes that offer flexibility in the forefoot area to allow for natural foot movement.
Balance and Stability
With three key principles in mind - coordination, proprioception, and strength - therapists can guide pediatric patients towards improved balance and stability during gait training.
Balance assessment is a critical component of pediatric mobility training, as it helps identify areas of weakness or instability. By assessing a child's ability to maintain balance in various positions and during different tasks, therapists can create targeted therapeutic interventions to address specific deficits.
These interventions may include exercises to improve coordination, such as balancing on one leg or walking on uneven surfaces, as well as activities to enhance proprioception, such as using balance boards or therapy balls.

Additionally, strength training exercises can help build the muscles necessary for maintaining stability during gait.
Through a comprehensive approach that addresses all three principles, therapists can empower pediatric patients to achieve greater balance and stability, allowing them to navigate their world with freedom and confidence.
Neurodevelopmental Techniques
One of the key components in pediatric mobility training is the integration of neurodevelopmental techniques to promote optimal motor development in children. These techniques are essential in helping children with movement disorders or delays to improve their mobility and reach their full potential. Neurodevelopmental techniques focus on facilitating normal movement patterns and enhancing motor skills through therapeutic interventions.
Here are five essential techniques used in pediatric mobility training:
Bobath Technique: This approach aims to normalize movement patterns and improve coordination through guided facilitation and inhibition techniques.
Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT): This technique involves restricting the use of the unaffected limb to encourage the use and development of the affected limb.
Neurodevelopmental Treatment (NDT): NDT focuses on guiding and facilitating movement patterns to promote more efficient and functional movement.

Sensory Integration Therapy: This technique uses sensory experiences to improve motor planning, coordination, and body awareness.
Task-Oriented Training: This technique focuses on practicing functional tasks to improve motor skills and independence.
Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy
The integration of Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT) as one of the top ten essential techniques in pediatric mobility training allows therapists to effectively encourage the use and development of the affected limb by restricting the use of the unaffected limb.
CIMT is a widely recognized and evidence-based intervention that has shown promising results in pediatric rehabilitation. By restraining the unaffected limb, therapists create a 'constraint' that forces the child to rely on and actively engage the affected limb, promoting neuroplasticity and functional recovery.
This technique not only helps improve motor skills but also fosters a sense of independence and freedom in children with mobility limitations.
Task-Oriented Training
Incorporating task-oriented training into pediatric mobility therapy programs allows therapists to systematically guide children through purposeful activities, fostering skill acquisition and functional independence. This approach focuses on specific tasks that are relevant to the child's daily life, such as walking, running, or climbing stairs. By analyzing the child's gait and identifying areas of need, therapists can tailor the training to address specific challenges and promote optimal movement patterns.
Task-oriented training offers several benefits for children with mobility issues:

- Improved motor control and coordination
- Enhanced muscle strength and endurance
- Increased confidence and self-esteem
- Greater participation in activities of daily living
- Promotion of long-term functional independence
Through task-oriented training and gait analysis, therapists can empower children to overcome physical limitations and achieve their full potential. This approach not only improves their mobility but also enhances their overall quality of life, allowing them to enjoy the freedom of movement that every child deserves.
Aquatic Therapy
By utilizing the buoyancy and resistance of water, aquatic therapy provides a unique therapeutic environment that promotes mobility, strength, and flexibility in pediatric patients.
Hydrotherapy, also known as water therapy or aquatic exercise, involves performing various exercises and activities in a pool or water-based environment under the guidance of a trained therapist.
The warm water helps relax muscles, reduce pain, and increase circulation, while the buoyancy of water reduces the impact on joints, making it an ideal therapy option for children with mobility challenges.
Additionally, the resistance provided by the water helps build muscle strength and improve cardiovascular fitness.
Swimming therapy, a form of aquatic therapy, focuses on enhancing swimming skills while also providing therapeutic benefits.
Overall, aquatic therapy offers a safe and enjoyable way for pediatric patients to improve their mobility and overall well-being.
Virtual Reality Interventions
Virtual reality interventions are an innovative approach to enhancing motor skills and providing immersive therapy experiences for pediatric patients. By using virtual reality technology, therapists can create virtual environments that simulate real-world scenarios, allowing children to engage in therapeutic activities in a fun and engaging way.
These interventions have the potential to improve coordination, balance, and overall mobility while providing a safe and controlled environment for rehabilitation.
Enhancing Motor Skills
One effective method for improving motor skills is through the use of innovative interventions that provide individuals with diverse opportunities for growth and development. These interventions focus on enhancing sensory integration and coordination exercises.
Here are five essential techniques that can help individuals enhance their motor skills:
Sensory integration activities: Engaging in activities that stimulate different senses, such as tactile, auditory, and visual, can improve sensory processing and motor coordination.
Balance training: Exercises that challenge balance and stability can enhance motor skills by improving core strength and coordination.
Fine motor exercises: Activities that target hand-eye coordination and dexterity, such as puzzles or threading beads, can improve fine motor skills.

Gross motor activities: Engaging in activities that involve large muscle groups, such as running or jumping, can enhance overall motor skills and coordination.
Task-specific training: Practicing specific tasks or movements repeatedly can help individuals refine their motor skills and improve coordination.
Immersive Therapy Experiences
Through the use of immersive therapy experiences, individuals can engage in virtual reality interventions that provide a unique and effective approach to enhancing their motor skills and overall therapeutic outcomes.
This innovative approach utilizes immersive therapy techniques to create a virtual environment where children can actively participate in therapeutic exercises and movements. By immersing themselves in this virtual world, children are able to engage in various activities that target specific motor skills, such as balance, coordination, and strength.
The interactive nature of virtual reality allows therapists to tailor the experience to each child's specific needs, providing a personalized and engaging therapy session. Additionally, virtual reality interventions can offer a sense of freedom and independence to children, as they can explore and interact with the virtual environment at their own pace.
Overall, immersive therapy experiences using virtual reality have the potential to revolutionize pediatric therapy by providing an effective and enjoyable way to enhance motor skills and improve therapeutic outcomes.
Home Modifications
When considering home modifications for individuals with mobility limitations, it is important to assess the accessibility and safety of the living environment. Home modifications play a crucial role in enhancing motor skills and promoting independence for those with mobility challenges.
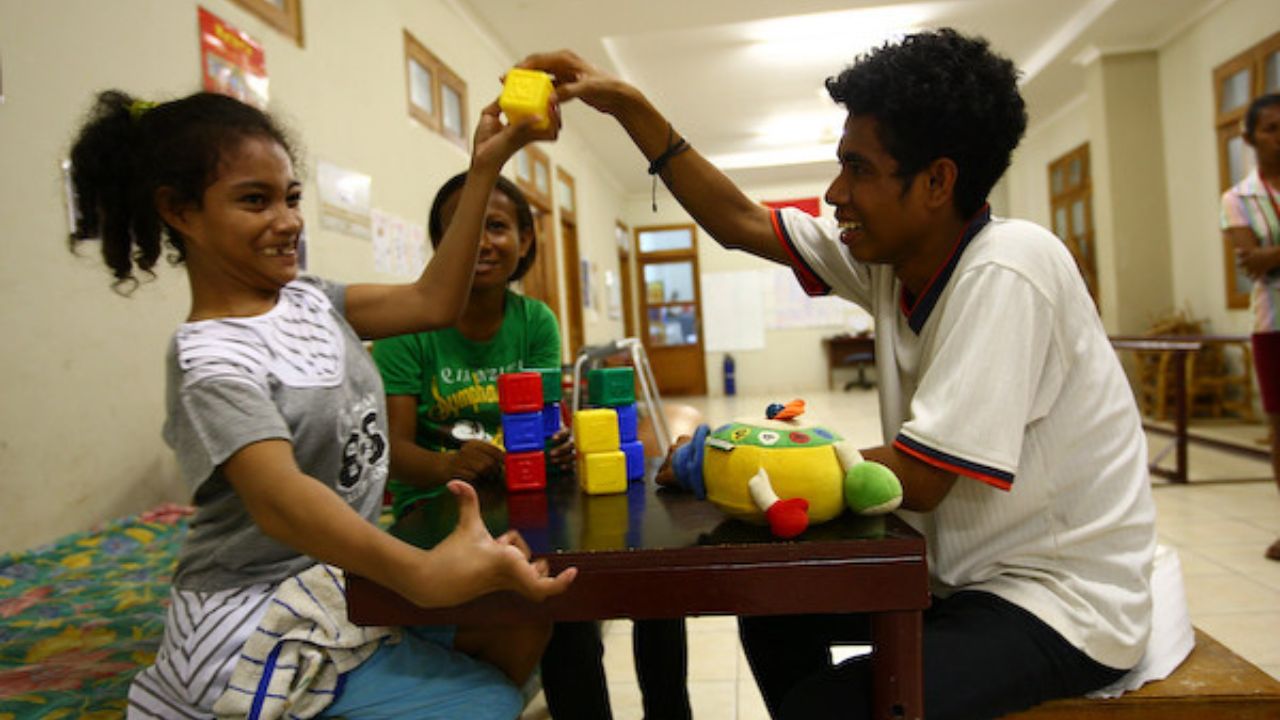

These modifications can range from simple adjustments to more extensive renovations, depending on the specific needs of the individual. Here are five essential considerations to ensure a safe and accessible home environment:
- Install grab bars in bathrooms and other areas where support is needed.
- Create wider doorways to accommodate wheelchairs and walkers.
- Install ramps or lifts to eliminate barriers and facilitate easy movement.
- Improve lighting throughout the house to prevent accidents and falls.
- Remove tripping hazards such as rugs and clutter to create a clear pathway.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Common Challenges Faced by Pediatric Patients During Mobility Training?
During mobility training, pediatric patients may face challenges such as limited strength, coordination, and balance. Parental involvement is crucial in addressing these challenges, providing support, and facilitating the child's progress in their mobility training journey.
How Can Parents Actively Participate in Their Child's Mobility Training?
Parental involvement in a child's mobility training is crucial for their progress. Active participation allows parents to understand the techniques used, reinforce them at home, and provide emotional support. This benefits the child's overall development and enhances the therapeutic intervention.
Are There Any Alternative Therapies or Interventions for Pediatric Mobility Training?
There are several alternative therapies and non-traditional interventions available for pediatric mobility training. These include acupuncture, hydrotherapy, animal-assisted therapy, yoga, and sensory integration therapy. These options can provide additional benefits and complement traditional techniques.
What Are the Potential Risks or Side Effects Associated With Certain Mobility Training Techniques?
When considering potential risks and side effects of mobility training techniques for pediatric patients, it is important to assess each technique individually. Common risks may include muscle strains or falls, while side effects could involve temporary discomfort or increased fatigue.
How Long Does It Typically Take for Children to Show Improvement in Their Mobility Skills Through Therapeutic Intervention?
The timeline for improvement in children's mobility skills through therapeutic intervention varies depending on various factors such as the severity of their condition, their age, and their commitment to the intervention program.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pediatric mobility training is a multifaceted approach that encompasses various techniques to promote independence and functional mobility in children.

By utilizing adaptive equipment, strengthening exercises, balance and gait training, neurodevelopmental techniques, task-oriented training, aquatic therapy, virtual reality interventions, and home modifications, healthcare professionals can provide comprehensive therapeutic interventions.
These techniques aim to enhance motor skills, improve balance and coordination, and maximize children's participation in daily activities.
By employing a knowledge-based, empathetic, and detail-oriented approach, healthcare professionals can effectively support children in achieving optimal mobility and independence.
 Mobility trainingHome Fitness RecoverySports Injury PreventionPersonal Physical TherapyOrthopedic SolutionsPrivacy PolicyTerms And Conditions
Mobility trainingHome Fitness RecoverySports Injury PreventionPersonal Physical TherapyOrthopedic SolutionsPrivacy PolicyTerms And Conditions
